Developing a Roadmap for Implementing Local Language Models
Abstract⌗
As the potential of AI becomes increasingly recognized, there is a growing demand for the implementation of Local Language Models (LLMs) in various organizations. This document aims to present a comprehensive plan to fulfill this requirement by outlining the available options and defining the objectives at each step of the system development process.
By addressing the need for running Local LLMs, this document provides valuable insights into the considerations involved in developing an effective system. The plan outlined herein serves as a roadmap for organizations seeking to leverage AI technology through the utilization of LLMs.
Introduction⌗
Large Language Models have seen a breakthrough in the overall performance and usefulness in the last few years. Since the introduction of the Transformer model in 2018 - Attention is all you need
[1706.03762] Attention Is All You Need
OpenAI is a public turn private company that takes the advantage of this method of training and produces a well known AI model: ChatGPT.
Which through multiple generations has increased its parameters from billions to trillions with tons of resources poured into training such models.
But because of the business advantage of such technology and resources they choose to keep those models private and only supply the public with API endpoints with limited access to the actual model.
However, there has been a growing demand for running Local LLMs, which are LLMs that can be hosted and used locally by organizations.
Running Local LLMs can provide several benefits for organizations.
Firstly, it offers more control and privacy over the data and models used. By hosting the LLM locally, organizations can ensure that sensitive information is not shared with external servers. This is particularly important for industries that deal with highly confidential data
Secondly, running Local LLMs can improve the speed and efficiency of AI applications. By eliminating the need to send data to external servers for processing, organizations can reduce latency. This is crucial for applications that require quick responses, such as customer support chatbots or recommendation systems.
The document aims to explore the process of running Local LLMs (Local Language Model) on private hardware. To accomplish this, the objective is divided into several steps that can be completed within a few months. Each step is accompanied by potential obstacles that should be addressed and assessed before moving on to the next step.
By breaking down the goal into manageable steps, the document provides a structured approach to implementing Local LLMs on private hardware. This approach allows for a systematic evaluation of potential challenges and ensures that they are resolved before progressing further. Ultimately, this method aims to facilitate the successful implementation of Local LLMs on private hardware within a reasonable timeframe.
The plan⌗
1- Setup development environment⌗
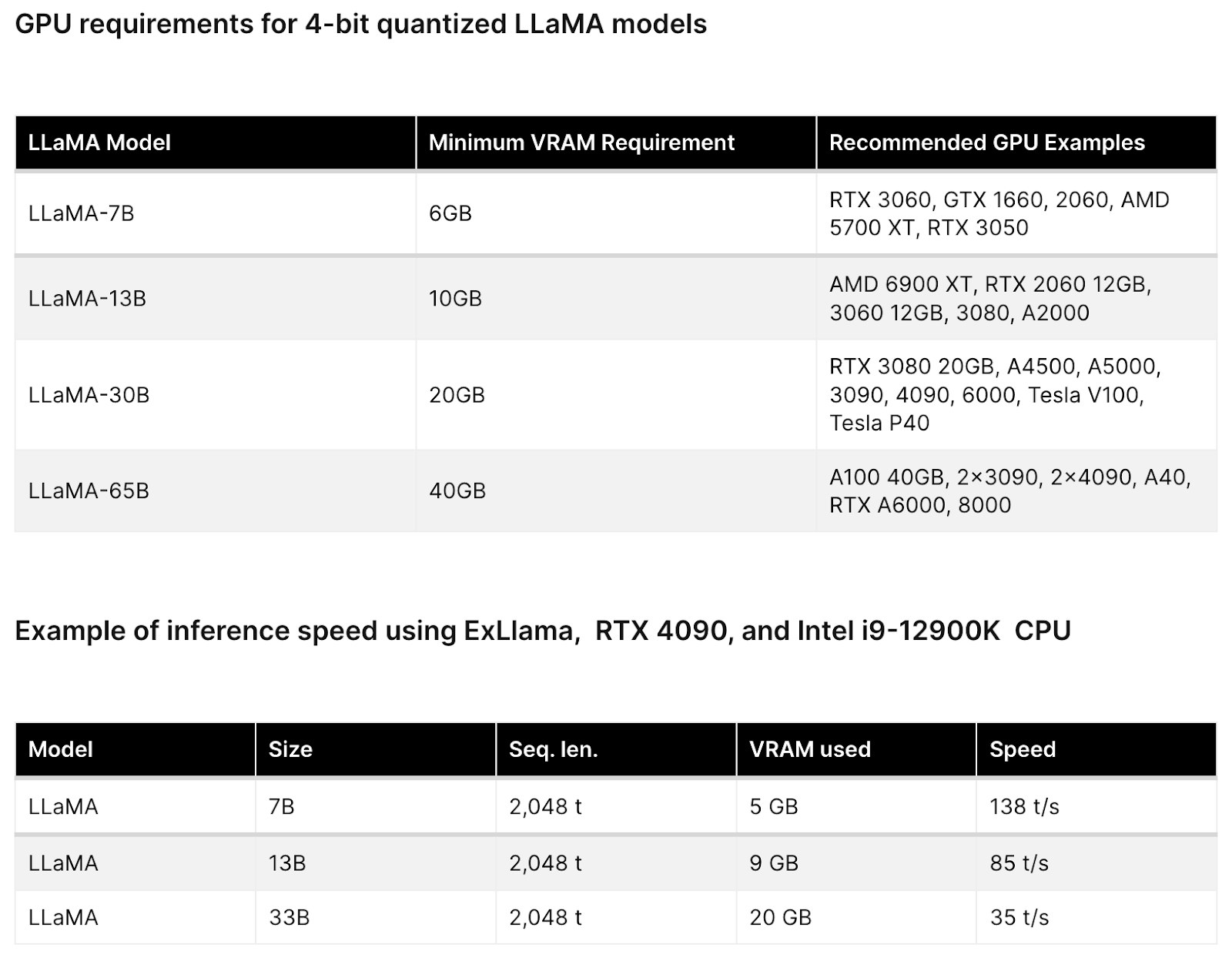
The environment is to kick start the project. To provide developers access to GPU resources to perform the experiments with LLMs.
There are 2 options:
On-Premise hardware⌗
| Machine | Cost |
|---|---|
| PC i9 13900K / 32GB RAM / VGA RTX 4060 8GB / SSD 512GB NVMe | $1,428 |
| PC i7 13700K / 32GB RAM / VGA RTX 3060 12GB / SSD 512GB | $1,105 |
Pros:
- Own the hardware, One time cost
- High security inside managed VPN
Cons:
- High initial cost
Cloud provided GPU⌗
| Cost per hour | Machine | Amount | Cost per month |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4~0.9$/hour | 1x RTX 4090 | 1 | 83~187$/month |
- Price * 8 hours/day * 26 days
Pros:
- Lower recurrent cost, pay per use
- Not require much setup in term of hardware
Cons:
- Outside the organization network
Proposal⌗
Budget to use Cloud Provided GPU to save starting cost. Develop a working environment that is resilient, can be easily set up and torn down multiple times.
Then we can move the setup into On-premise.
Objective⌗
Understand the cost model. Effectiveness of each setup.
Metrics to consider:
- CPU, GPU, Memory usage
- Tokens per second
2- Training / Evaluation with Public data⌗
Initially, it is important to acknowledge that the full potential of all the Language Models (LLMs) may not be known at the outset. Each LLM possesses distinct properties and exhibits varying behavior when generating inferences. To gain a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities, it is necessary to conduct preliminary testing using publicly available data before integrating them into our workflow and specific use cases.
Public data can be sourced from various platforms, including public websites and documents, among others. By utilizing this data, we can evaluate the performance of the LLMs and assess their suitability for our intended applications. This evaluation process can be facilitated by employing modified versions of the evaluation models utilized in HuggingFace LLM ranking.
By conducting thorough testing and evaluation, we can make informed decisions regarding the selection and integration of LLMs into our workflow. This approach ensures that the chosen models align with our requirements and exhibit optimal performance in generating accurate and reliable inferences.
Evaluation methods⌗
- AI2 Reasoning Challenge (25-shot) - a set of grade-school science questions.
- HellaSwag (10-shot) - a test of common sense inference, which is easy for humans (~95%) but challenging for SOTA models.
- MMLU (5-shot) - a test to measure a text model’s multitask accuracy. The test covers 57 tasks including elementary mathematics, US history, computer science, law, and more.
- TruthfulQA (0-shot) - a test to measure a model’s propensity to reproduce falsehoods commonly found online. Note: TruthfulQA in the Harness is actually a minima a 6-shots task, as it is prepended by 6 examples systematically, even when launched using 0 for the number of few-shot examples.
Objective⌗
The objective of this step is to acquire proficiency in utilizing the models and fine-tuning their output to align with our specific requirements. This entails gaining a deep understanding of the models’ capabilities and exploring techniques to optimize their performance for our intended use cases. Additionally, establishing a feedback loop is essential to continuously improve and automate the development process.
By actively engaging with the models and iteratively refining their output, we can ensure that they are effectively tailored to meet our specific needs. This feedback loop enables us to identify areas for improvement, make necessary adjustments, and enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the development process. Ultimately, this step aims to leverage the models’ capabilities while continuously refining and automating their usage to achieve optimal results.
It needs to perform tasks such as:
- Summarization
- Classification
- Information Extraction
- Formatted output (JSON, Python REPL, etc.)
- Code Generation
At this step, we also interest in the strength and weakness of each models for a given domain like:
- Multiple languages
- General knowledge like Math, Science, Law, etc.
- Logical thinking and Reasoning
To streamline the automation process and effectively utilize multiple Language Models (LLMs), we will implement MLOps practices.
3- Build application⌗
The development of the application is a pivotal aspect of this plan. It is essential to establish a collaborative relationship with the users to ascertain the specific requirements of the task they intend to automate. This process involves actively engaging with the users to identify their needs and expectations.
Once the requirements are gathered, the next step is to design and program a workflow that comprises modules that utilize the Language Models (LLMs) to process the relevant information. These modules should be tailored to effectively address the identified requirements.
Lastly, the modules need to be interconnected to create a cohesive process that enhances the users’ work and aids them in achieving their final goals. The application should serve as a valuable tool that streamlines their tasks and facilitates their overall productivity.
Objective⌗
- Solve real world problem
- Provide a feedback loops to continue evolve the whole process
Tools and Resources⌗
Interactive UI for trial and configuration⌗
Oobabooga⌗
Features
- 3 interface modes: default, notebook, and chat
- Multiple model backends: transformers, llama.cpp, ExLlama, AutoGPTQ, GPTQ-for-LLaMa
- Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models
- LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA
- Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama 2, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others
- Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4
- 8-bit and 4-bit inference through bitsandbytes
- CPU mode for transformers models
- DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 inference
- Extensions
- Custom chat characters
- Very efficient text streaming
- Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA
- Nice HTML output for GPT-4chan
- API, including endpoints for websocket streaming (see the examples)
Serving API for inference⌗
llama.cpp⌗
GitHub - ggerganov/llama.cpp: Port of Facebook’s LLaMA model in C/C++
The main goal of llama.cpp is to run the LLaMA model using 4-bit integer quantization
OpenLLM⌗
GitHub - bentoml/OpenLLM: Operating LLMs in production
With OpenLLM, you can run inference with any open-source large-language models, deploy to the cloud or on-premises, and build powerful AI apps.
Application development⌗
Langchain⌗
Power your applications with Large Language Models
LangChain’s flexible abstractions and extensive toolkit enables developers to harness the power of LLMs.
Langsmith (beta)⌗
Platform for Monitor, Debug, Test & Evaluate multiple workflow and LLMs